-40%
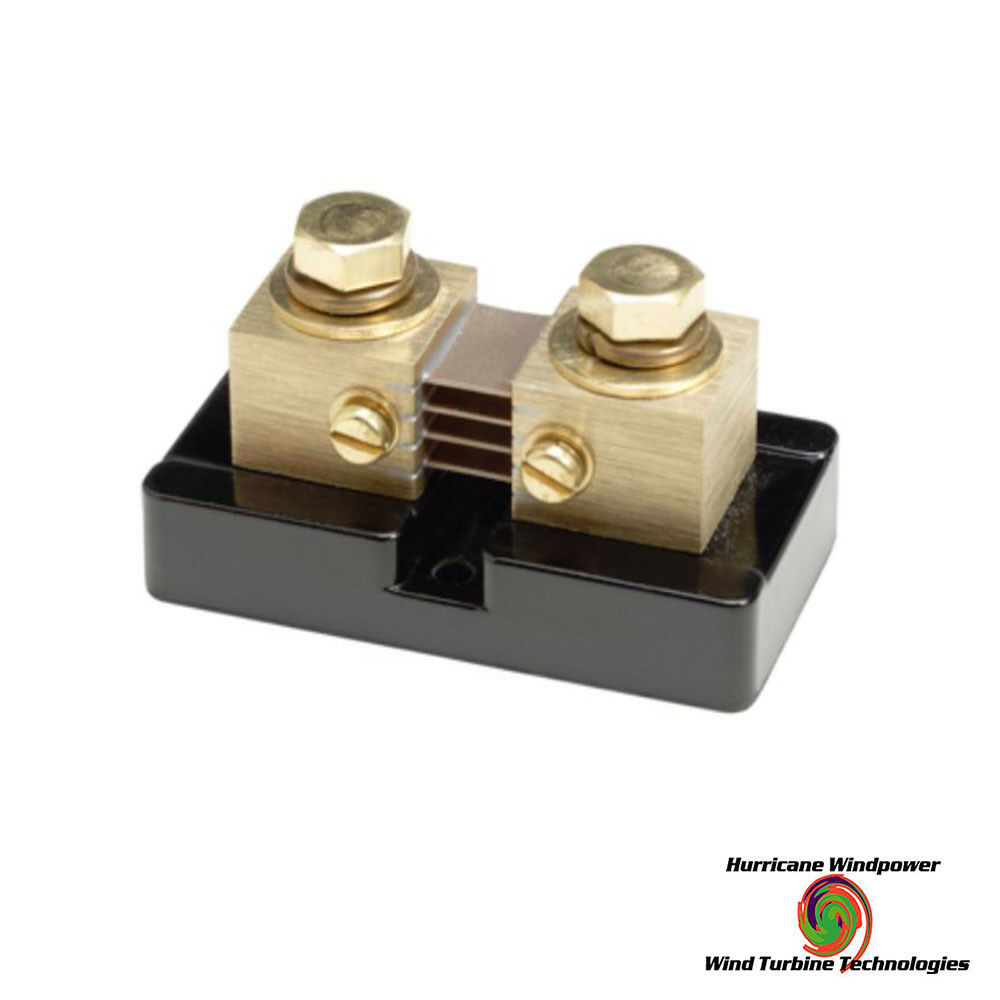
DELTEC 500A 50MV DC SHUNT FOR CURRENT MONITORING METERS FOR MIDNITE SOLAR BOGART
$ 23.76
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
DELTEC 500A 50MV DC SHUNT FOR CURRENT MONITORING METERS FOR MIDNITE SOLAR BOGARTDeltec SHUNT 500A/50MV
What is a shunt?
A shunt is a very small, accurately-known, low resistance resistor used to measure current. Meters & Battery Monitors use shunts to measure amps and amp-hours. The shunt is placed in series with the load so that it can measure the current flowing through it. Because the resistance is known, the current be calculated based on measuring the voltage drop across the shunt.
For loads less than 70 amps, use the 100A, 100mV Shunt for Current Monitoring Meters. The 500A, 50mV Shunt for Current Monitoring Meters is recommended for loads up to 400 amps. For larger loads that will not exceed 900 amps, use the Bogart Engineering 1000A, 100mV Shunt.
50mV/500amp includes taptite mounting screws. Has two 8-32 tapped holes on one end to attach a bus bar. This is the industry standard shunt. Can be connect directly to a Midnite Solar Whiz Bang Jr .
SPECIFICATIONS:
Resistance:
"500 Amp at 50 millivolts", or 0.1 milliohm.
Max. steady state current, amps:
410 Amperes
Thermal time constant:
18 minutes
Overload current:
If normally operated at less than 300 amps, it will take overloads to 500 amps for durations of less than 5 minutes.
Physical characteristics:
Has a plastic base 3.25 x 1.75 in. with two mounting holes .205 "dia, 1.25" apart o.c. 1.75 inches overall height. High current connections are made to two bolts (3/8"-16) which are 1.50 in. apart (o.c).
HOW A SHUNT WORKS
A shunt is necessary in order to measure amps and amp-hours with the TriMetric battery monitor. A shunt is an accurate, very low resistance resistor which is placed "in line" with the wire carrying the current to be measured. With the TriMetric, it is usually placed in the negative wire from the battery bank, such that all the current going into the battery (charging) or out (discharging) must pass through it. Connected in this way it will be set up to monitor "net" amp-hours in and out of the battery. (It also could be placed in series with the negative wire coming from a solar array--or other charging source--in which case it would measure only the solar array current, if that were desired--to show total solar "amp hours" production.) The shunt needs to be placed near the batteries; since these wires carry very high currents the wires from the batteries must be kept short to minimize electrical losses.
SHUNT RESISTANCE
When current flows through the shunt, a small voltage is developed across the shunt which is proportional to the current flow. The TriMetric battery monitor accurately measures this very low voltage and converts it to the "amps" reading on the meter. The resistance, which is the ratio between the voltage across the shunt and the current flowing through it, is a constant for any particular shunt--and is one of its important parameters. For most substances, resistance is usually described in "ohms", however for some reason shunts are described by the voltage drop that occurs with a certain current: for example: "50 millivolts at 500 amperes." However the meter only cares about the ratio-which is the resistance--so a 500Amp/50 millivolt shunt is equivalent, from the TriMetric's view, to a 250Amp/25 millivolt shunt. They both have a resistance of 0.1 milliohm, or one ten thousandth of an ohm.
HOW TO SET A SHUNT UP CORRECTLY
The TriMetric is designed to use either a 500 Amp/50 millivolt (0.1 milliohm) or 100 Amp/100 millivolt (1.0 milliohm) shunt. The latter shunt delivers 10 times the voltage for a given current flow through the shunt, so the meter can show an extra digit of current resolution (down to 0.01 amp) compared with the 500 Amp/50 millivolt shunt, which displays a minimum current of 0.1 amp. To make the TriMetric read "amps" and "amp-hours" correctly, you must tell the TriMetric which shunt is being used. This is done by programming either an "L" (low) or "H" (high) in one of the program modes. ("L" for the 100A/100 mV shunt, and "H" for the 500 A/50 mV shunt.) For how to do this refer to TriMetric instructions under "How to set efficiency factor and shunt type".
Source: Bogart Engineering
Hurricane Wind Power
2019
Corporate America Today
2019 Best Off-Grid
Renewable Energy
Product Supplier - USA
UP TO 50% DISCOUNTS
TOP BRANDS
Payment
Shipping
Returns
Payment
Shipping
Returns
We accept payment by any of the following methods:
PayPal
Please pay as soon as possible after winning an auction, as that will allow us to post your item to you sooner!
We offer
Fast shipping
on all orders!
Your order will be dispatched within 1-3 working day of receiving payment (Monday-Friday) and you should expect to receive it one or two days after dispatch (for orders sent RM 1st Class).
In the very unlikely event that your item is lost or damaged during post, then WE are responsible and will issue either a full refund or replacement.
If you are not 100% satisfied with your purchase, you can return the product and get a full refund or exchange the product for another one, be it similar or not.
You can return a product for up to 14 days from the date you purchased it.
Any product you return must be in the same condition you received it and in the original packaging. Please keep the receipt.
See our other items
Thank you for visiting our Ebay store!
Deltec SHUNT 500A/50MV What is a shunt? A shunt is a very small, accurately-known, low resistance resistor used to measure current. Meters & Battery Monitors use shunts to measure amps and amp-hours. The shunt is placed in series with the load so that it can measure the current flowing through it. Because the resistance is known, the current be calculated based on measuring the voltage drop across the shunt. For loads less than 70 amps, use the 100A, 100mV Shunt for Current Monitoring Meters. The 500A, 50mV Shunt for Current Monitoring Meters is recommended for loads up to 400 amps. For larger loads that will not exceed 900 amps, use the Bogart Engineering 1000A, 100mV Shunt. 50mV/500amp includes taptite mounting screws. Has two 8-32 tapped holes on one end to attach a bus bar. This is the industry standard shunt. Can be connect directly to a Midnite Solar Whiz Bang Jr . SPECIFICATIONS ---Resistance: "500 Amp at 50 millivolts", or 0.1 milliohm. ---Max. steady state current, amps: 410 Amperes ---Thermal time constant: 18 minutes ---Overload current: If normally operated at less than 300 amps, it will take overloads to 500 amps for durations of less than 5 minutes. ---Physical characteristics: Has a plastic base 3.25 x 1.75 in. with two mounting holes .205 "dia, 1.25" apart o.c. 1.75 inches overall height. High current connections are made to two bolts (3/8"-16) which are 1.50 in. apart (o.c). HOW A SHUNT WORKS A shunt is necessary in order to measure amps and amp-hours with the TriMetric battery monitor. A shunt is an accurate, very low resistance resistor which is placed "in line" with the wire carrying the current to be measured. With the TriMetric, it is usually placed in the negative wire from the battery bank, such that all the current going into the battery (charging) or out (discharging) must pass through it. Connected in this way it will be set up to monitor "net" amp-hours in and out of the battery. (It also could be placed in series with the negative wire coming from a solar array--or other charging source--in which case it would measure only the solar array current, if that were desired--to show total solar "amp hours" production.) The shunt needs to be placed near the batteries; since these wires carry very high currents the wires from the batteries must be kept short to minimize electrical losses. SHUNT RESISTANCE When current flows through the shunt, a small voltage is developed across the shunt which is proportional to the current flow. The TriMetric battery monitor accurately measures this very low voltage and converts it to the "amps" reading on the meter. The resistance, which is the ratio between the voltage across the shunt and the current flowing through it, is a constant for any particular shunt--and is one of its important parameters. For most substances, resistance is usually described in "ohms", however for some reason shunts are described by the voltage drop that occurs with a certain current: for example: "50 millivolts at 500 amperes." However the meter only cares about the ratio-which is the resistance--so a 500Amp/50 millivolt shunt is equivalent, from the TriMetric's view, to a 250Amp/25 millivolt shunt. They both have a resistance of 0.1 milliohm, or one ten thousandth of an ohm. SETTING UP THE TRIMETRIC FOR CORRECT SHUNT The TriMetric is designed to use either a 500 Amp/50 millivolt (0.1 milliohm) or 100 Amp/100 millivolt (1.0 milliohm) shunt. The latter shunt delivers 10 times the voltage for a given current flow through the shunt, so the meter can show an extra digit of current resolution (down to 0.01 amp) compared with the 500 Amp/50 millivolt shunt, which displays a minimum current of 0.1 amp. To make the TriMetric read "amps" and "amp-hours" correctly, you must tell the TriMetric which shunt is being used. This is done by programming either an "L" (low) or "H" (high) in one of the program modes. ("L" for the 100A/100 mV shunt, and "H" for the 500 A/50 mV shunt.) For how to do this refer to TriMetric instructions under "How to set efficiency factor and shunt type". Source: Bogart Engineering
DELTEC 500A 50MV DC SHUNT FOR CURRENT MONITORING METERS FOR MIDNITE SOLAR BOGART
Deltec SHUNT 500A/50MV
What is a shunt?
A shunt is a very small, accurately-known, low resistance resistor used to measure current. Meters & Battery Monitors use shunts to measure amps and amp-hours. The shunt is placed in series with the load so that it can measure the current flowing through it. Because the resistance is known, the current be calculated based on measuring the voltage drop across the shunt.
For loads less than 70 amps, use the 100A, 100mV Shunt for Current Monitoring Meters. The 500A, 50mV Shunt for Current Monitoring Meters is recommended for loads up to 400 amps. For larger loads that will not exceed 900 amps, use the Bogart Engineering 1000A, 100mV Shunt.
50mV/500amp includes taptite mounting screws. Has two 8-32 tapped holes on one end to attach a bus bar. This is the industry standard shunt. Can be connect directly to a Midnite Solar Whiz Bang Jr .
SPECIFICATIONS
Resistance:
"500 Amp at 50 millivolts", or 0.1 milliohm.
Max. steady state current, amps:
410 Amperes
Thermal time constant:
18 minutes
Overload current:
If normally operated at less than 300 amps, it will take overloads to 500 amps for durations of less than 5 minutes.
Physical characteristics:
Has a plastic base 3.25 x 1.75 in. with two mounting holes .205 "dia, 1.25" apart o.c. 1.75 inches overall height. High current connections are made to two bolts (3/8"-16) which are 1.50 in. apart (o.c).
HOW A SHUNT WORKS
A shunt is necessary in order to measure amps and amp-hours with the TriMetric battery monitor. A shunt is an accurate, very low resistance resistor which is placed "in line" with the wire carrying the current to be measured. With the TriMetric, it is usually placed in the negative wire from the battery bank, such that all the current going into the battery (charging) or out (discharging) must pass through it. Connected in this way it will be set up to monitor "net" amp-hours in and out of the battery. (It also could be placed in series with the negative wire coming from a solar array--or other charging source--in which case it would measure only the solar array current, if that were desired--to show total solar "amp hours" production.) The shunt needs to be placed near the batteries; since these wires carry very high currents the wires from the batteries must be kept short to minimize electrical losses.
SHUNT RESISTANCE
When current flows through the shunt, a small voltage is developed across the shunt which is proportional to the current flow. The TriMetric battery monitor accurately measures this very low voltage and converts it to the "amps" reading on the meter. The resistance, which is the ratio between the voltage across the shunt and the current flowing through it, is a constant for any particular shunt--and is one of its important parameters. For most substances, resistance is usually described in "ohms", however for some reason shunts are described by the voltage drop that occurs with a certain current: for example: "50 millivolts at 500 amperes." However the meter only cares about the ratio-which is the resistance--so a 500Amp/50 millivolt shunt is equivalent, from the TriMetric's view, to a 250Amp/25 millivolt shunt. They both have a resistance of 0.1 milliohm, or one ten thousandth of an ohm.
SETTING UP THE TRIMETRIC FOR CORRECT SHUNT
The TriMetric is designed to use either a 500 Amp/50 millivolt (0.1 milliohm) or 100 Amp/100 millivolt (1.0 milliohm) shunt. The latter shunt delivers 10 times the voltage for a given current flow through the shunt, so the meter can show an extra digit of current resolution (down to 0.01 amp) compared with the 500 Amp/50 millivolt shunt, which displays a minimum current of 0.1 amp. To make the TriMetric read "amps" and "amp-hours" correctly, you must tell the TriMetric which shunt is being used. This is done by programming either an "L" (low) or "H" (high) in one of the program modes. ("L" for the 100A/100 mV shunt, and "H" for the 500 A/50 mV shunt.) For how to do this refer to TriMetric instructions under "How to set efficiency factor and shunt type".
Source: Bogart Engineering
Hurricane Wind Power
2019
Corporate America Today
2019 Best Off-Grid
Renewable Energy
Product Supplier - USA
UP TO 50% DISCOUNTS
TOP BRANDS
See our other items
Payment
We accept payment by any of the following methods:
PayPal
Please pay as soon as possible after winning an auction, as that will allow us to post your item to you sooner!
Shipping
We offer
Fast shipping
on all orders!
Your order will be dispatched within 1-3 working day of receiving payment (Monday-Friday) and you should expect to receive it one or two days after dispatch (for orders sent RM 1st Class).
In the very unlikely event that your item is lost or damaged during post, then WE are responsible and will issue either a full refund or replacement.
Returns
If you are not 100% satisfied with your purchase, you can return the product and get a full refund or exchange the product for another one, be it similar or not.
You can return a product for up to 14 days from the date you purchased it.
Any product you return must be in the same condition you received it and in the original packaging. Please keep the receipt.
Thank you for visiting our Ebay store!
Deltec SHUNT 500A/50MV
What is a shunt?
A shunt is a very small, accurately-known, low resistance resistor used to measure current. Meters & Battery Monitors use shunts to measure amps and amp-hours. The shunt is placed in series with the load so that it can measure the current flowing through it. Because the resistance is known, the current be calculated based on measuring the voltage drop across the shunt.
For loads less than 70 amps, use the 100A, 100mV Shunt for Current Monitoring Meters. The 500A, 50mV Shunt for Current Monitoring Meters is recommended for loads up to 400 amps. For larger loads that will not exceed 900 amps, use the Bogart Engineering 1000A, 100mV Shunt.
50mV/500amp includes taptite mounting screws. Has two 8-32 tapped holes on one end to attach a bus bar. This is the industry standard shunt. Can be connect directly to a Midnite Solar Whiz Bang Jr .
SPECIFICATIONS
Resistance:
"500 Amp at 50 millivolts", or 0.1 milliohm.
Max. steady state current, amps:
410 Amperes
Thermal time constant:
18 minutes
Overload current:
If normally operated at less than 300 amps, it will take overloads to 500 amps for durations of less than 5 minutes.
Physical characteristics:
Has a plastic base 3.25 x 1.75 in. with two mounting holes .205 "dia, 1.25" apart o.c. 1.75 inches overall height. High current connections are made to two bolts (3/8"-16) which are 1.50 in. apart (o.c).
HOW A SHUNT WORKS
A shunt is necessary in order to measure amps and amp-hours with the TriMetric battery monitor. A shunt is an accurate, very low resistance resistor which is placed "in line" with the wire carrying the current to be measured. With the TriMetric, it is usually placed in the negative wire from the battery bank, such that all the current going into the battery (charging) or out (discharging) must pass through it. Connected in this way it will be set up to monitor "net" amp-hours in and out of the battery. (It also could be placed in series with the negative wire coming from a solar array--or other charging source--in which case it would measure only the solar array current, if that were desired--to show total solar "amp hours" production.) The shunt needs to be placed near the batteries; since these wires carry very high currents the wires from the batteries must be kept short to minimize electrical losses.
SHUNT RESISTANCE
When current flows through the shunt, a small voltage is developed across the shunt which is proportional to the current flow. The TriMetric battery monitor accurately measures this very low voltage and converts it to the "amps" reading on the meter. The resistance, which is the ratio between the voltage across the shunt and the current flowing through it, is a constant for any particular shunt--and is one of its important parameters. For most substances, resistance is usually described in "ohms", however for some reason shunts are described by the voltage drop that occurs with a certain current: for example: "50 millivolts at 500 amperes." However the meter only cares about the ratio-which is the resistance--so a 500Amp/50 millivolt shunt is equivalent, from the TriMetric's view, to a 250Amp/25 millivolt shunt. They both have a resistance of 0.1 milliohm, or one ten thousandth of an ohm.
SETTING UP THE TRIMETRIC FOR CORRECT SHUNT
The TriMetric is designed to use either a 500 Amp/50 millivolt (0.1 milliohm) or 100 Amp/100 millivolt (1.0 milliohm) shunt. The latter shunt delivers 10 times the voltage for a given current flow through the shunt, so the meter can show an extra digit of current resolution (down to 0.01 amp) compared with the 500 Amp/50 millivolt shunt, which displays a minimum current of 0.1 amp. To make the TriMetric read "amps" and "amp-hours" correctly, you must tell the TriMetric which shunt is being used. This is done by programming either an "L" (low) or "H" (high) in one of the program modes. ("L" for the 100A/100 mV shunt, and "H" for the 500 A/50 mV shunt.) For how to do this refer to TriMetric instructions under "How to set efficiency factor and shunt type".
Source: Bogart Engineering